
Working at a factory in Luxembourg
Forget the stereotypical factory image; here, a diverse team keeps things running. From the highly skilled technicians operating cutting-edge machinery to the production workers ensuring precision on the assembly line, each role is crucial.
We will explore the fundamental aspects of factory work, detailing the required training and skills for a production worker. Additionally, we'll shed light on the diverse positions available, the demand for production workers in Luxembourg, avenues for job seekers, typical salaries, and the necessary documentation for foreigners looking to embark on a career in this dynamic sector.
What is the demand for production workers in Luxembourg?
Luxembourg, with its diverse industries, consistently presents a high demand for production workers, making this profession advantageous due to abundant job opportunities.
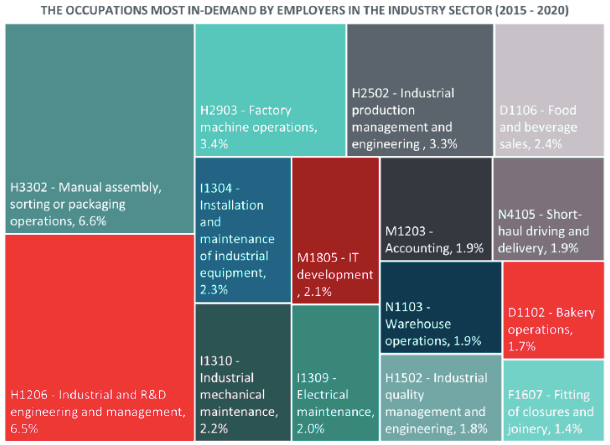
Some statistics
To assess the demand for these roles in Luxembourg, a sectoral study by the Ministry of Labour (MT) and the Employment Development Agency (ADEM) spanning from 2015 to 2020 sheds light on the outlook for production worker positions.
According to the study, manual assembly workers are the most sought-after, constituting 6.6% of the demand in the industrial sector. Machine operators follow closely, ranking third with a demand share of 3.4%.
What does factory work consist of?
Factory work encompasses a diverse range of roles, ranging from production workers to skilled technicians, team leaders, engineers, managers, and even the factory director. This article will focus on the often underappreciated, yet crucial roles commonly grouped under the title of production workers.
Production workers operate in an industrial setting, typically on assembly or production lines. Positioned at the beginning of the production line, they work under the supervision of a production manager.
Depending on the company's structure, production workers may be responsible for one or multiple stages of production, such as packaging, assembly, manufacturing, preparation, or inspection. In their designated areas, these workers execute highly specific tasks, following protocols and instructions outlined in their job descriptions.
Production workers play a pivotal role in ensuring product quality and the seamless operation of manufacturing machines. Assigned to specific machines or equipment, they must guarantee optimal functionality, addressing both production efficiency and health and safety concerns. Reporting any anomalies related to their workstations or defects in product quality is part of their duties. Maintenance operations, including cleaning and lubrication, are also performed to sustain equipment functionality.
The primary missions of a production worker include but are not limited to, preparing production according to work orders and plans. This involves studying instructions, blueprints, and orders from workshop supervisors, setting up and adjusting necessary machines, and managing material input and output. Ensuring production involves actively participating in manufacturing processes, upholding hygiene standards, monitoring product quality, completing production documentation, and reporting any anomalies.
Additionally, they play a role in packaging and storage by packaging produced items and organizing their storage. Finally, production workers also need to do the maintenance of the workstation which involves keeping it clean, maintaining machines, and organizing the workspace. The specific tasks may vary depending on the position, work area, and industry sector within the company.
Production workers find employment in various industrial sectors, including but not limited to:
- Metallurgical industry
- Rubber industry
- Textile, clothing, leather, and footwear industry
- Food industry
- Information technology, electronics, and electrical equipment industries
- Wood, paper, and furniture industries
- Chemical and pharmaceutical industries
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace industry
Training and skills required to work at production
To some extent, the qualifications sought by recruiters depend on the industry in which the production worker operates and the specifics of the position they are to undertake.
In certain specific sectors and for particular roles, recruiters may require a level of education equivalent to high school, valuing the candidate's experience and motivation.
Technical training qualifications are also highly appreciated, especially when the industry involves stringent quality standards.
Commonly sought qualifications for production operator roles include CAP (Certificat d'Aptitude Professionnelle), BEP (Brevet d'Études Professionnelles), Bac Pro (Baccalauréat Professionnel), or CQP (Certificat de Qualification Professionnelle) in a specific field. One example of possible studies in this field in Luxembourg is the Bac Pro Production Line Operator (PLP).
Upon joining a company, on-site training is generally required to adapt to the specific role. Depending on an individual's skills and experience, the adaptation period can range from one to six months before becoming fully operational.
Continuous training modules exist to enhance experience in handling specific machinery such as CNC machines, basic maintenance, and special machining.
In addition to formal education, a production worker must possess multiple skills and competencies, many developing throughout training and experience.
Production workers in Luxembourg combine formal education, on-the-job training, and diverse skills to ensure that manufacturing processes run seamlessly in various industry sectors. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential to thrive in this dynamic and essential field of work.
What types of positions can be found in this area?
Industrial production includes a variety of jobs, often referred to as production operators or industrial laborers.
We will explore several distinct roles within the field of industrial production









Where to find a job as a production worker?
If you're looking for a career in industry and are wondering where to find factory jobs in Luxembourg, we'll answer your questions, explore the major job boards, and highlight major companies in Luxembourg that are actively recruiting production workers.
Job portals
For a comprehensive exploration of the job market, the internet serves as the prime resource, hosting numerous employment portals with thousands of job listings. These platforms enable users to filter job offers based on desired sector, location, education level, or required work experience.


Luxembourg establishments recruiting production workers
In Luxembourg, numerous industries actively seek production workers for diverse positions, including millers, binders, sheet metal workers, welders, turners, and more. However, it's common for companies to fill these roles through temporary employment agencies rather than direct hiring. This practice makes it less practical to target specific companies, as they often don't directly advertise such positions.
The use of temporary agencies for these roles is prevalent due to the fluctuating demand for production workers. Seasonal variations, project-based needs, and the nature of industrial production contribute to this dynamic. While this approach provides flexibility for companies, it may pose challenges for workers seeking long-term stability.
Noteworthy temporary employment agencies in Luxembourg that frequently recruit production workers include:
What is the salary of production workers in Luxembourg?
Determining a singular salary range for production workers in Luxembourg is challenging due to the diverse roles within this field, where experience significantly influences earnings. For a general overview, we can refer to Paylab, which provides salary ranges for various positions in industrial production in Luxembourg.
| Role | Minimum (euros) | Maximum (euros) |
| Packer | 1,600 | 3,917 |
| Machine Operator | 1,807 | 3,887 |
| Foundry worker | 1,873 | 4,105 |
| Metalworker | 2,339 | 4,754 |
| Cutter/Grinder/Polisher | 2,339 | 4,907 |
| Milling-Machine Operator | 2,384 | 5,049 |
| Turner | 2,410 | 4,945 |
| Machine Setter | 2,696 | 5,320 |
| Welder | 2,707 | 5,312 |
| CNC Machine Setter | 2,993 | 5,135 |
Wage to count on
Usually, factory workers in Luxembourg recieve from 1,600 to 5,000 euros roughly. This wage is based on the calculations of the job portal.
What papers do you need as a foreigner?
For European nationals, the process of working in Luxembourg is relatively straightforward, given the freedom to live and work in any European country. However, if you are not a European national, navigating the paperwork becomes essential.
The requirements vary based on your circumstances, distinguishing between employed and self-employed roles. Additionally, familial situations, such as having a Luxembourgish or European partner, can impact the process.


Work permit in Luxembourg
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of jobs are available for production workers in Luxembourg?
Production workers in Luxembourg can find a diverse range of jobs, including roles such as manual assemblers, machine operators, borers, millers, sandblasters, extruders, coilers, sheet metal workers, boilermakers, TIG welders, and lathe operators. The industrial sector in Luxembourg offers various opportunities for those interested in manufacturing and production.
What does factory work in Luxembourg typically involve?
Factory work in Luxembourg involves tasks such as manual assembly, machine operation, precision machining, surface treatment, welding, and the transformation of raw materials into finished products. Production workers may work in industries such as metallurgy, textiles, food, electronics, automotive, and more, contributing to the manufacturing processes in these sectors.
What qualifications and skills are required for production workers in Luxembourg?
Qualifications vary depending on the specific role, but commonly sought certifications include CAP, BEP, Bac Pro, or CQP in a relevant field. Technical training and continuous learning are essential. Skills include adherence to safety and hygiene standards, physical fitness, precision, vigilance, teamwork, time management, and stress resistance.
What is the demand for production workers in Luxembourg?
Source: emploi.ouest-france.fr, www.orientation-pour-tous.fr, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.hellowork.com, www.groupelip.com, www.leparisien.fr, fr.indeed.com, www.orientation.lu, adem.public.lu, www.paylab.com
We took photos from these sources: ADEM, Mobijob, Lalit Kumar, Unsplash